The top 3 skills required in 2020 as predicted by the World Economic Forum are complex problem solving, critical thinking and creativity. For 2030 these are predicted to be creativity, critical thinking and decision making in that order. These skills are referred to as Higher Order Thinking Skills and are seen as key to being successful in any field in the years ahead.
The origins of higher order thinking are in the fields of philosophy and psychology. While the field of philosophy has grown through discourse and argumentation, the field of psychology has evolved from a tradition of experimentation and research. Philosophers have used logical reasoning and perfections of thinking to decide what to believe and do, and psychologists have studied the thinking process and how this process can help people make sense out of their experience by constructing meaning and imposing structure. Psychologists emphasize problem solving and philosophers reflective thinking and logic.
Educationists have built on these contsructs to evaluate how to encourage and develop higher order thinking skills the student community. The constructivist theory recognises that students need to be exposed to learning experiences that enable them to construct their own knowledge and promote their thinking skills (Cobb, 1994; Driver, Asoko, Leach, Mortimer, & Scott, 1994). Higher order thinking can be viewed as the strategy — the setting of meta-objectives; whereas critical, systemic thinking are the tactics — the activities needed to achieve the proclaimed objectives. Blooms taxonomy has been often referred to while creating learning objectives in the cognitive domain.
Constructing one’s own learning is especially critical in the area of Creativity. Nurturing creativity involves helping students to generate ideas or hypotheses, test them and communicate the results; think adventurously (step into the unknown); and invent, discover, be curious, experiment and explore.
To start off with it is essential that there is constructive alignment between objectives and skills. Next, it is imperative that there are specific opportunities in the curriculum planned for this learning and development. Additionally, these have to be strategically located at the required learning stages. And finally, one has to link the skills to be learned with the employability needs of the student in the years ahead. Based on these, the 3 critical variables of student learning identified were identified for Pearl students as below
a. Graduate Outcomes
b. Prioritized higher order thinking skills
c. Key Locations in the curriculum
A study was conducted over 3 years to identify learning experiences that promote creativity, critical thinking, innovation and other higher order skills. These were mapped with graduate outcomes and industry needs. Next, the overall curriculum was revised to include specific spaces to enable this learning. Based on the above Pearl Academy has developed a meta-curriculum to ensure total learning of each of its student, based on identified outcomes and desired higher order thinking skills. This meta curriculum is called the PEARL TOTAL LEARNING SYSTEM and is a layer under all the disciplinary learning modules to ensure holistic learning and enhancement of higher order thinking. Interested academics may look at this process and outcome as an example that could be used elsewhere as well.
This Total Learning System ensures that ALL students experience learning, that helps them develop higher order thinking skills required to learn in the present and the future, as well as to help them be professionals and make effective choices during their careers and lives. Key innovations as a part of this learning system are a full year of multidisciplinary attitude based learning, common core modules for interdisciplinary learning, Open Labs in every semester, Service as a fundamental conscience, International Lab, Industry Live Project and Future Labs.
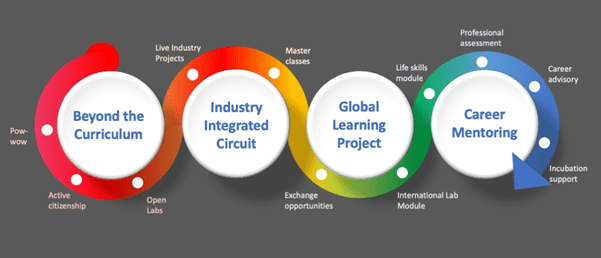
The Pearl Total Learning System has 4 pillars addressing learning needs based on future employability. All students across disciplines go through this learning system in their academic journey.
a. INDUSTRY INTEGRATED CIRCUIT — a series of engagement with the industry that ensures readiness for the industry and the development of complex problem solving, creativity and innovation
b. GLOBAL LEARNING PROJECT — international opportunities including student exchanges, projects with students from around the world, international faculty and international online modules that ensure that every student has an international exposure and develops a global context aiming at judgement, cognitive flexibility, emotional intelligence and creativity.
c. CAREER MENTORING — specific interventions during the student lifecycle that helps them identify their strengths and development areas, their career goals and respect for values & ethics of the profession. Through this they develop critical thinking, emotional intelligence and service orientation
d. BEYOND THE CURRICULUM — These are supra curricular spaces created for forward-looking courses and experiences that will give students the edge that they need to manage their careers in tomorrow’s environment
Each of these pillars within the meta curriculum, hold a series of experiences and learning which sets students up, to succeed in lifelong, self-directed learning, in the productive careers they may choose, and in continuing to grow throughout their lives, as the world continues to shift. Key to the PTLS is robust alliances with the industry, international partners and the continuous development of faculty to enable them to deliver the curriculum. If anyone wants to know more please visit this link https://pearlacademy.com/pearl-total-learning-system/ or contact the author.
(This article was first published on Medium.com)